What are the manufacturing processes for silicone parts?
Upload Time:
Oct 31, 2025
What are the production processes for silicone parts? Due to their outstanding physical and chemical properties, such as high elasticity, resistance to high and low temperatures, excellent electrical insulation and chemical stability, silicone parts are widely used in various fields including medicine, electronics, automobiles, aerospace, etc. From simple buttons and sealing rings to complex medical implants and precision electronic components, silicone parts are manufactured through diverse processes designed to meet the demands of various applications. Today, Prime Silinktech Silicone will guide you through the production methods for silicone parts.

I. Compression Molding
Compression molding is one of the most commonly used processes in silicone part production. This method involves placing mixed silicone raw material into a mold, where it is vulcanized into shape through heating and pressure. Material preparation for compression molding includes mixing and kneading raw silicone rubber, curing agents, and colorants. Mold design and fabrication must be tailored to the part's shape and dimensions, typically made from steel to ensure high precision and durability.
During the moulding process, the mould is placed within a vulcanising machine for heating and pressurisation. Under specific temperature and pressure conditions, the silicone raw material undergoes a vulcanisation reaction to form the desired shape. Following demoulding, post-processing steps such as trimming flash, cleaning, and inspection are required. The molding process has high production efficiency and precise product dimensions. It is suitable for mass production, but the cost of the molds is high, and the product shapes are limited.
II. Extrusion Moulding
Extrusion moulding is a continuous production process for silicone components. It involves extruding raw silicone material through an extruder into the desired shape, followed by cooling and cutting to form the final product. Similar to compression moulding, material preparation for extrusion moulding includes mixing and kneading of raw silicone rubber, curing agents, and colour masterbatch.
Extruders typically comprise a screw, barrel, die head, and heating system. The appropriate extruder is selected and calibrated according to the shape and dimensions of the component. During extrusion, silicone material is propelled towards the die by the rotating screw, where it is forced through a mould to form the desired shape. Extruded silicone parts undergo subsequent processes including cooling and cutting. Cooling may be achieved via water or air, while cutting can be performed manually or automatically.
The extrusion moulding process offers high production efficiency and consistent part geometry, making it suitable for continuous manufacturing. However, dimensional accuracy is relatively low, and moulding costs are comparatively high.
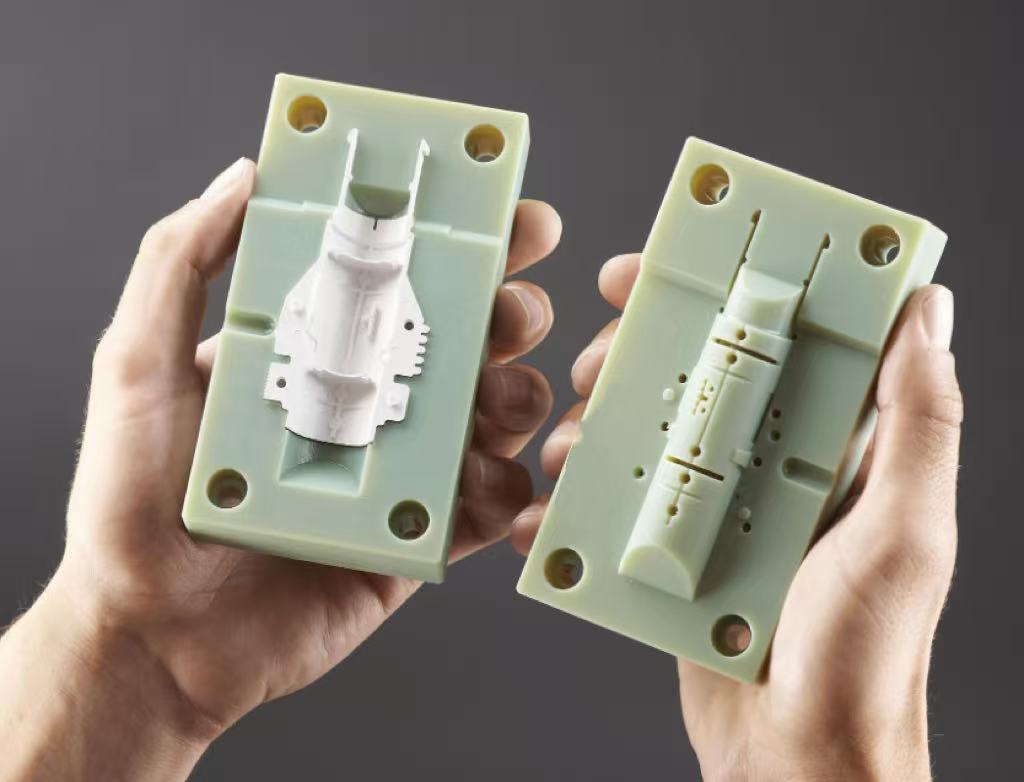
III. Injection Molding
Injection molding is a high-precision manufacturing process for silicone parts. It involves injecting silicone material into a mold, then shaping it through heating and cooling.
The composition of an injection moulding machine includes the injection system, clamping system, heating system, and cooling system. During the injection moulding process, the pre-compounded silicone material is fed into the machine and injected into the mould via the injection system. Under specific temperature and pressure conditions, a vulcanisation reaction occurs, forming the desired shape. Following demoulding, post-processing steps such as trimming flash, cleaning, and inspection are required. The injection moulding process offers high production efficiency and dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for large-scale production. However, it entails higher moulding costs and equipment investment.

IV. Drip Molding
Drip molding is a manual process for producing silicone parts. It involves dripping silicone raw material into a mold, then shaping it through heating and curing. Material preparation includes mixing and kneading raw silicone rubber, curing agents, and colorants. Molds can be silicone, metal, or plastic, with shapes and sizes customized as needed. Drip molding operations can be performed manually or using a drip molding machine, with the volume and placement of silicone controlled according to product specifications. After heating and curing, demolding and post-processing steps follow. This process offers simple operation and low cost, making it suitable for small-batch production. However, it features low production efficiency and relatively lower dimensional accuracy.
V. Other Production Processes
In addition to the four main production processes mentioned above, the production of silicone parts also includes processes such as solid-state hot pressing molding, liquid injection molding, calendering, pouring, and coating.
Solid-state hot-pressing molding utilizes the temperature and pressure of an oil press to mold the product through a mold. It is suitable for single-color silicone products, with low cost and high output, but the product structure is not flexible. Liquid injection molding involves pressing the A and B component raw materials into the injection machine barrel to mix, and then injecting them into the hot mold cavity for molding. The molding temperature is low, the output is high, and it is easy for automated production, but the raw material cost is relatively high.The calendering process employs a calender to compress silicone raw material into sheets of predetermined shape and thickness, suitable for manufacturing thin silicone products, though with relatively low production efficiency. The casting process involves pouring silicone directly onto a product or mould, removing the product after drying and curing to form a mould, ideal for creating smooth or simple items. The coating process involves uniformly applying silicone material to specific object surfaces, providing multiple functions such as wear resistance, protection, insulation, waterproofing, and dustproofing.
The production processes for silicone parts are diverse, each offering distinct advantages and applications. Compression moulding, extrusion moulding, and injection moulding are suited to high-volume production with excellent efficiency, though tooling costs are relatively high. Dip moulding offers straightforward operation and low cost, making it suitable for small batches, though production efficiency is low. Processes such as solid-state hot pressing, liquid injection moulding, calendering, casting, and coating are appropriate for producing silicone components with specific shapes and applications.

Relevant News